Background and Purpose:
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of remote sensing and GIS to manage urban ecosystems. The study takes place in West Africa which is a region that is experiencing high rates of urbanization. These two types of software can be used as a way to visualize and predict spatial features such as landscape, vegetation cover, water bodies, and human settlements as they change over time.
Methods:
The study analyzes three sites along the Ivory Coast: Abidjan, Accra, and Lagos. Image data from Google Earth Engine and USGS Earthexplorer were obtained. The image data were then analyzed to determine the Built-Up Index (permeable surfaces), Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, and Normalized Difference Water Index.
Results and Discussion:
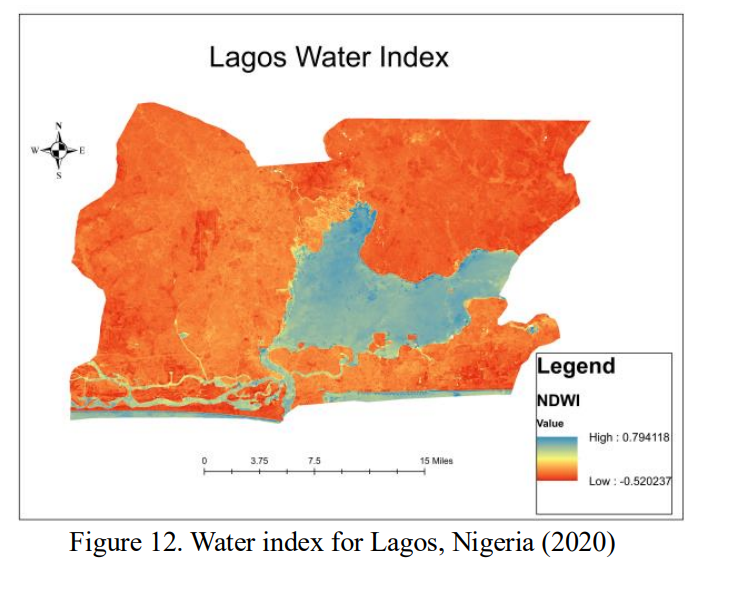
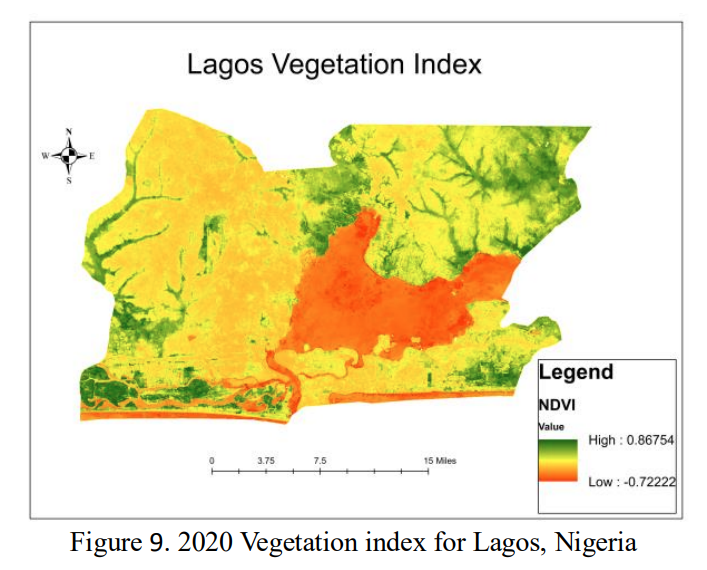
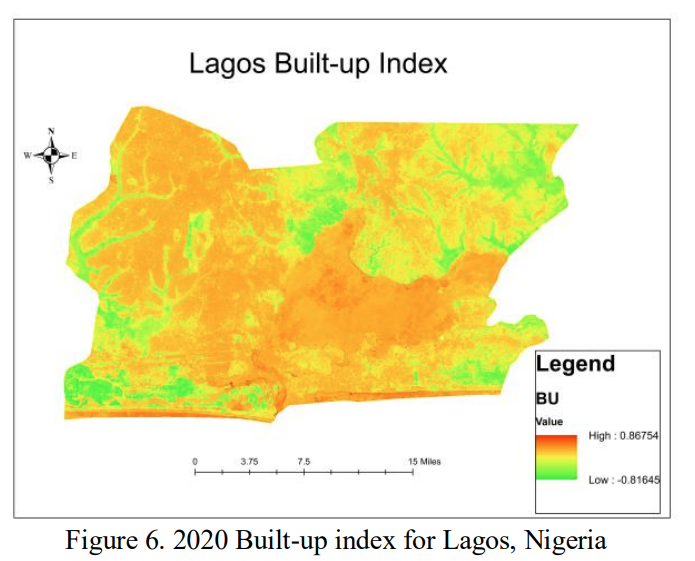
The final results of the study were maps generated through remote sensing and GIS data that compare the three indexes mentioned in the paragraph above. The discussion highlighted that an increase in the Built-Up Index leads to a decrease in the other two indexes which points to negative effects from urban areas. The study then reiterates the usefulness in using GIS and remote sensing to create management plans for urban ecosystems.
Reasons for Selecting:
I have an interest in GIS and the data science aspect of ecology. I saw this study was fairly recent and involved something relevant to the class as well as my personal interest. I have some background knowledge of GIS and remote sensing but I wanted to learn more about new methods and how this topic specifically relates to urban wildlife management.
Critiques:
My initial thought was that this study was fairly short. Each of the sections were only a few paragraphs long and the bulk of the article’s length was taken up by images and references. The results and discussion were combined into one section that was less than a third of a page long. I would have liked to see more in depth explanations of each section. Also, the study didn’t seem like it discovered anything new or exciting. They just selected data that they wanted to represent and plugged it into ArcGIS. To me, it appeared that they were more so demonstrating what the software that can be used for rather than a new method.
References:
Oppong, J., Ning, Z. H., Twumasi, Y., Antwi, R. A., Anokye, M., Ahoma, G., Annan, J., Namwamba, J. B., Loh, P., and Akinrinwoye, C.: THE INTEGRATION OF REMOTE SENSING AND GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM (GIS) IN MANAGING URBAN ECOSYSTEMS, Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci., XLVIII-M-3-2023, 169–175, https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLVIII-M-3-2023-169-2023, 2023.